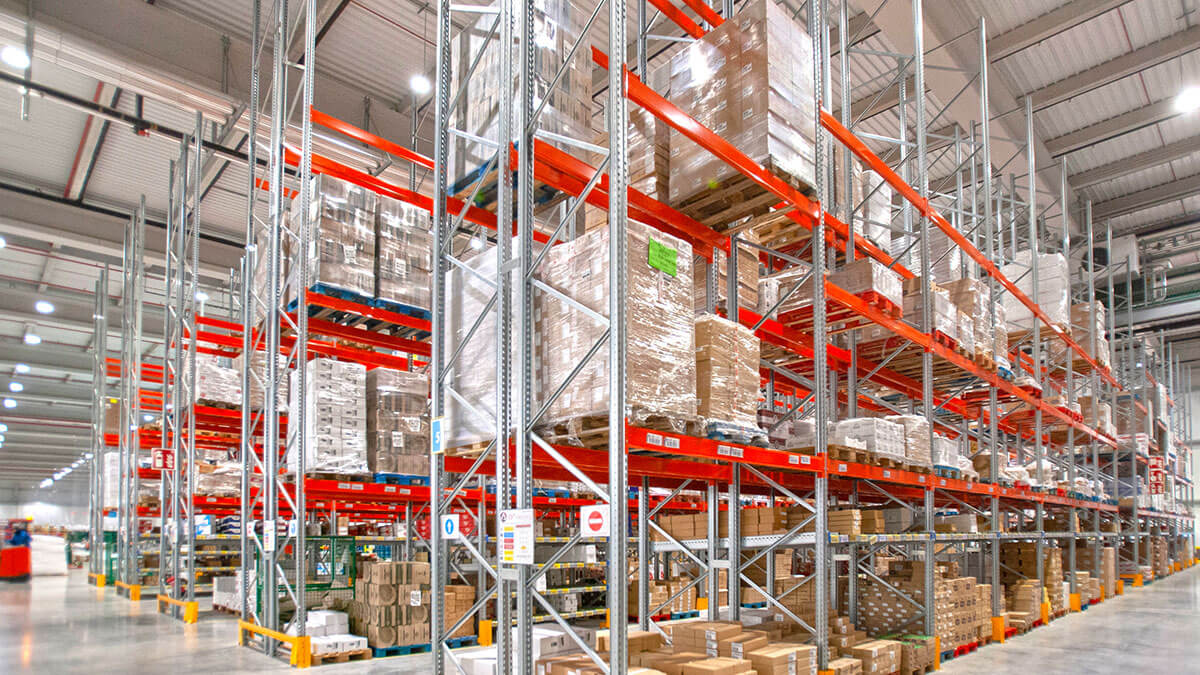
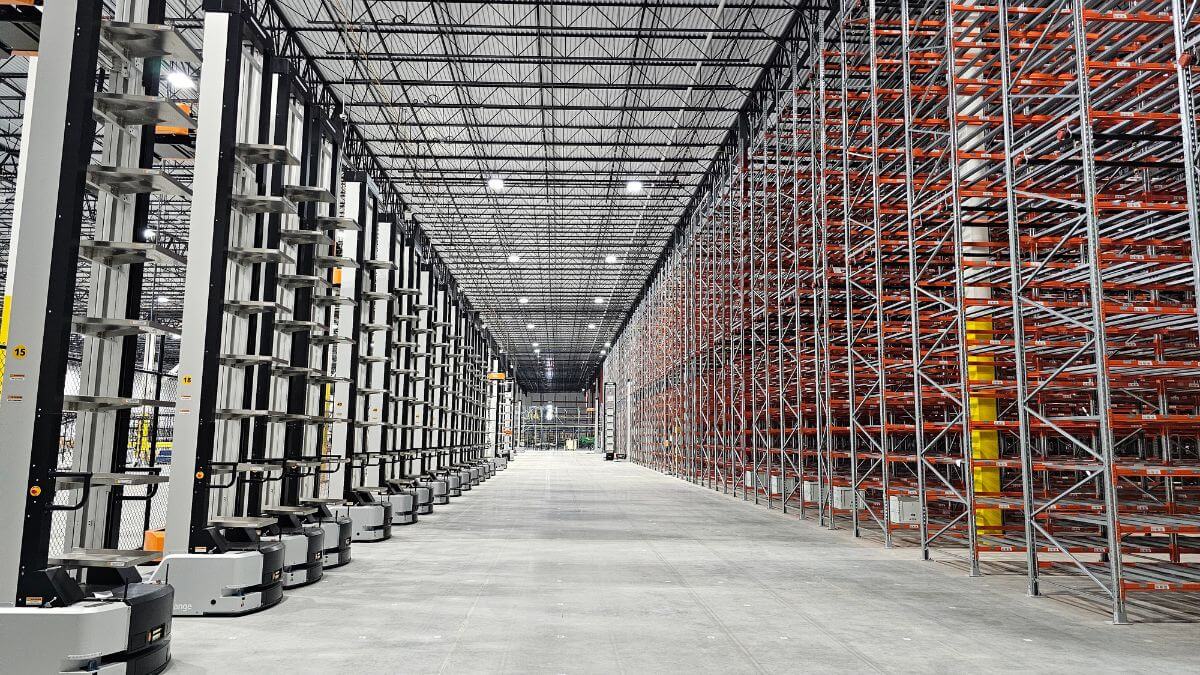
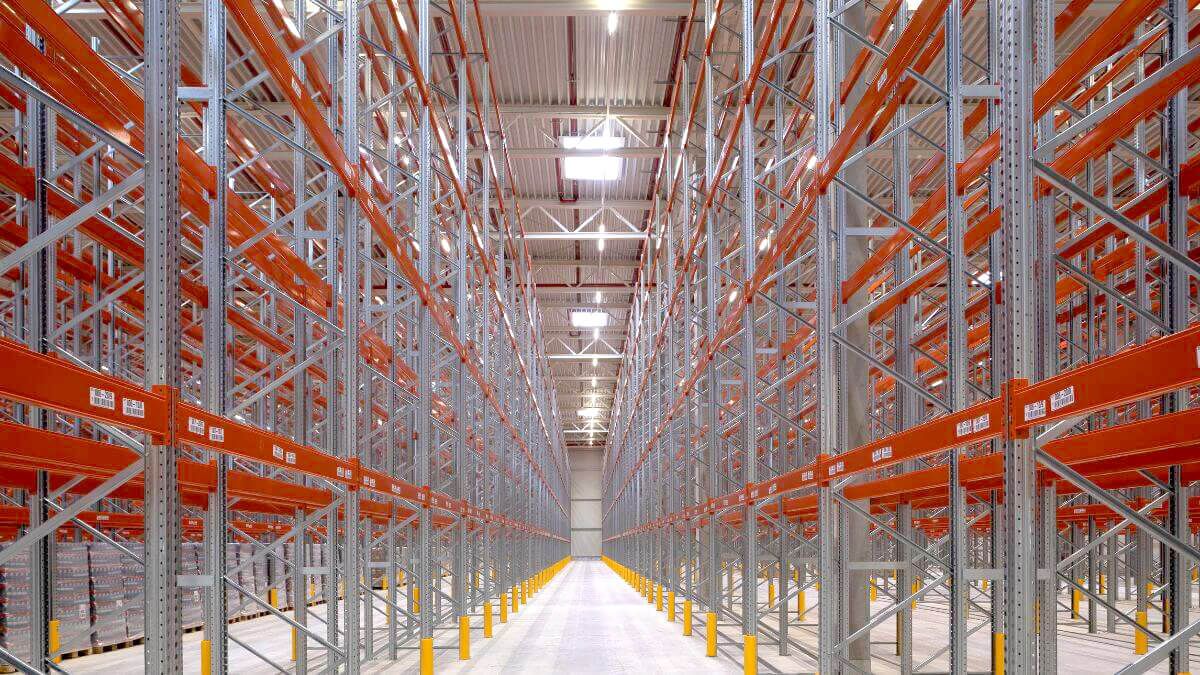
The vast majority of warehouses and distribution centres organise the distribution of their storage by installing Pallet Racking. The racking designed to store pallets optimises the available space and adapts to each company’s storage needs.
We analyse below the different types of pallet racking that can be installed in a warehouse and outline their characteristics and differences.
What is pallet racking?
Pallet racking is the system of grouping goods on pallets or other auxiliary elements to create a unit load that facilitates their storage and transport in the different phases of the supply chain.
It emerged during the Second World War to optimise transport and was originally only manufactured in wood.
Nowadays, it is about grouping the most used goods in warehouses and logistics in general, with most of the racking designed to store heavy loads specifically designed for the storage of pallet loads.
Pallet loads play a key role in almost all the logistic stages of the company, in both their handling inside the warehouse and in the transport stages.
There is a wide variety of types of pallets according to their dimensions or manufacturing material; however, the vast majority comply with standard measurements for which both industrial racking and forklifts and the rest of the tools and machinery involved in their handling are designed.
Major advantages of pallet racking
The palleting of goods for their subsequent storage on industrial racking has several advantages that can be summarised below as:
- Optimisation of loading and unloading times
- Compacting of goods and better use of available space
- Greater safety in transport of products
- Greater flexibility for their transport and handling
- Simplicity for stock and inventory control
- Reduced handling, transport and storage costs
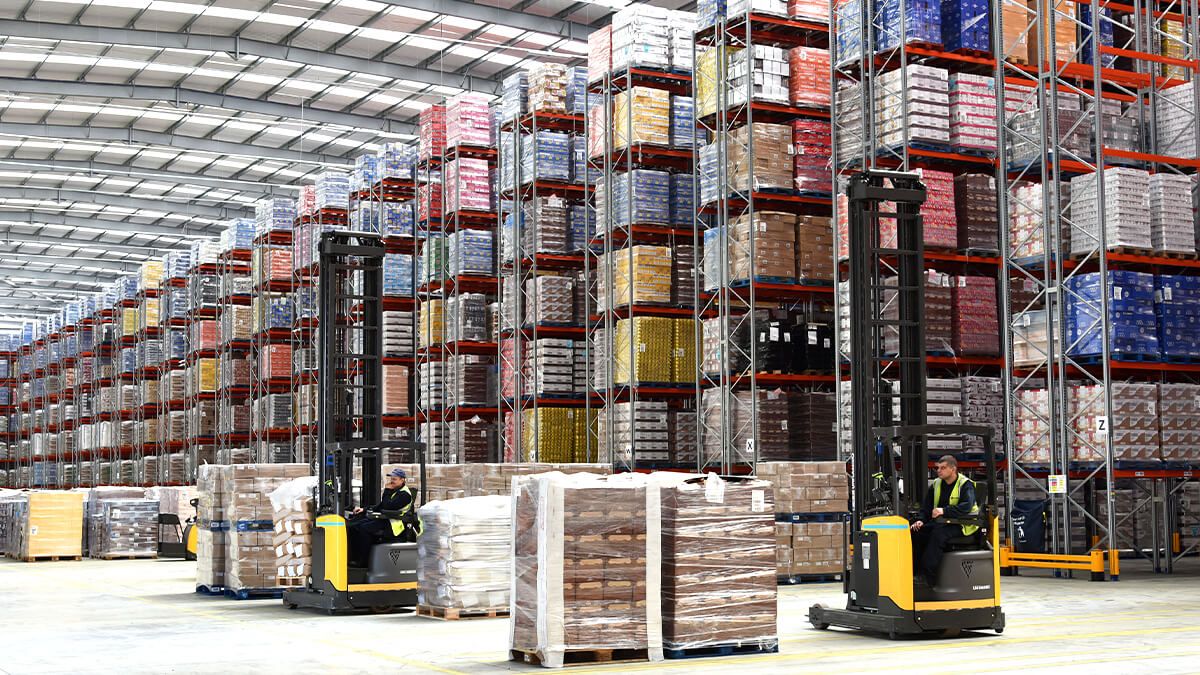

Choice between a selective or compact system
Among the wide variety of pallet storage systems set out below, there are two major types of racking in particular, firstly, selective storage systems (or with direct access) and, secondly, compact storage systems, which aim to increase the density of the racking to expand warehouse capacity.
Before weighing up the most suitable pallet racking option, the company must determine its storage characteristics and its current context. In this phase, it should be evaluated whether to prioritise the selection of a system that fully optimises the available space because our warehouse has a reduced surface area or very high per square metre floor price, or, if in its case, the available space is not a problem and the aim is to prioritise easy and quick access to the unit loads.
The type of product to store, inventory management to be performed, stock rotation, etc. must then be considered.
The most compact storage systems are the automated or semi-automated solutions (such as the AR Shuttle, the Clad-Rack Warehouses or the automated systems with stacker cranes) which we will not discuss in this list, focusing on non-automated pallet racking instead.
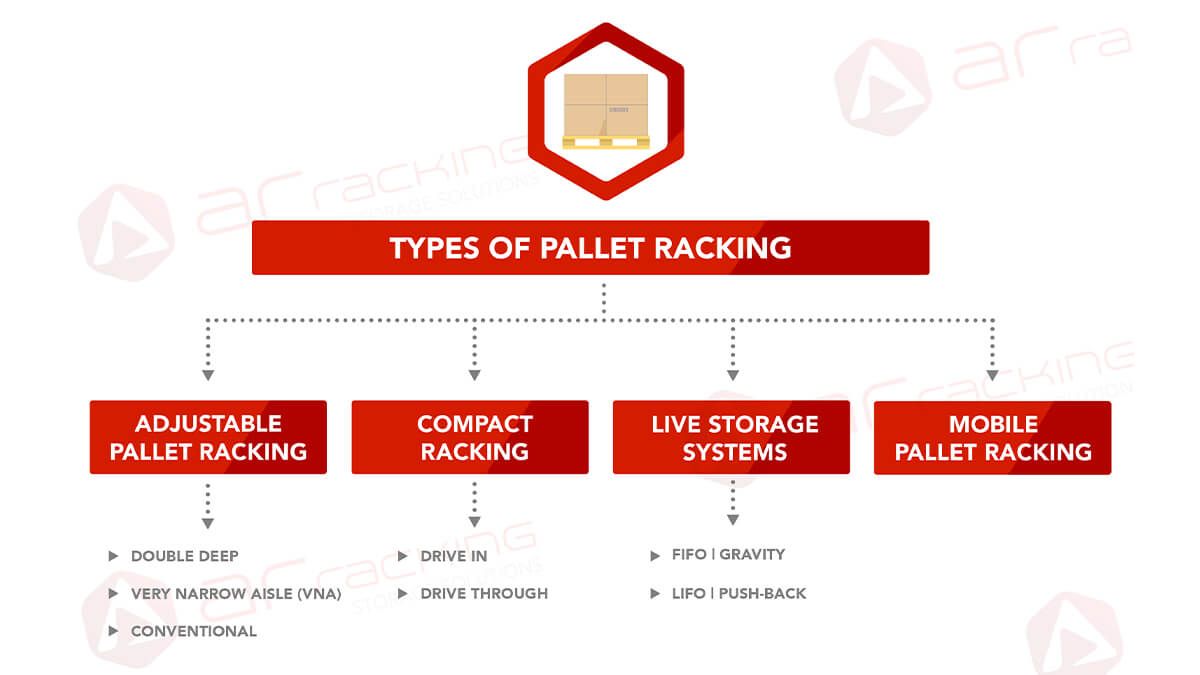
What are the main types of Pallet Racking?
The different types of pallet racking include the following systems:
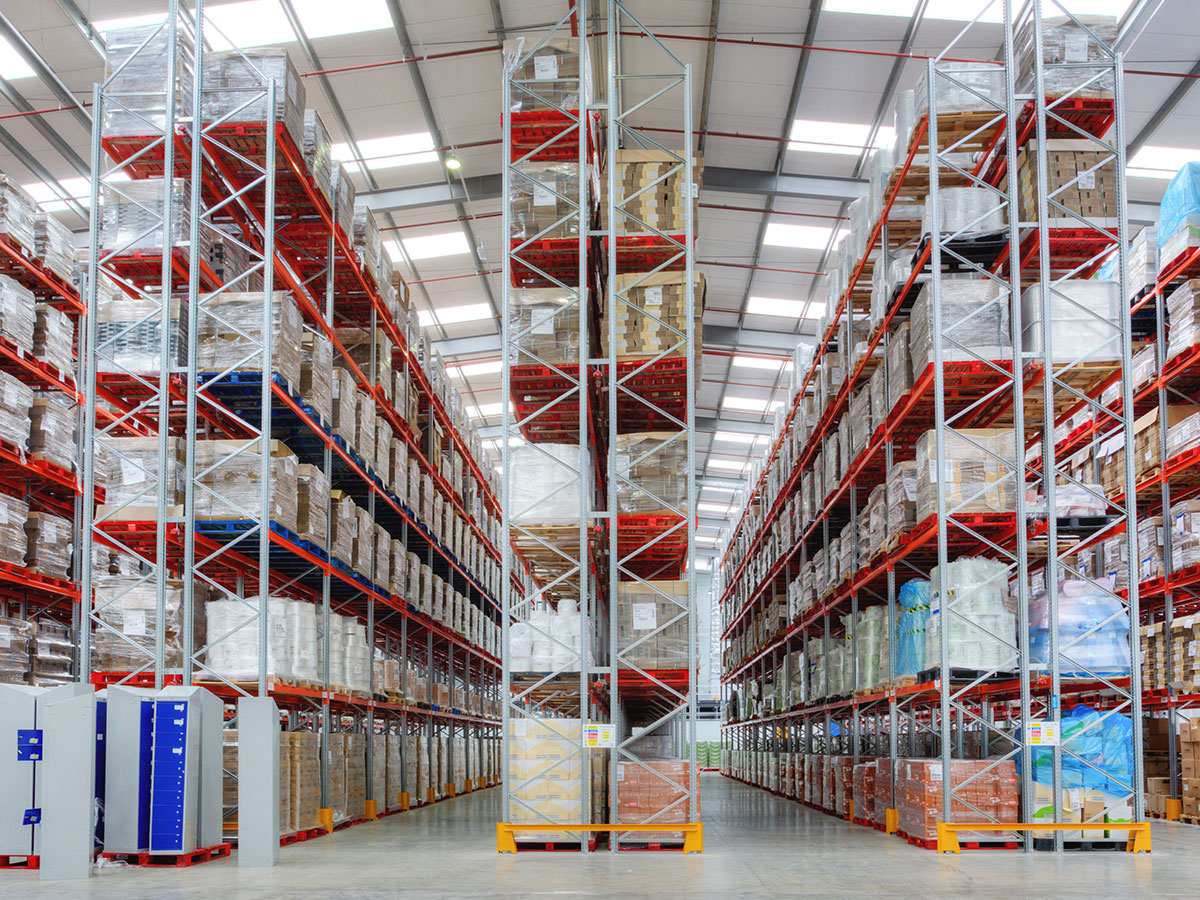
Adjustable Pallet Racking
This is the most common and simplest pallet racking system, and is designed to mechanically store pallets using forklifts that run parallel to the rows of racking.
It is not a compact system, so it requires quite a wide surface for its installation. Its main advantage is direct and quick access to all the unit loads stored, as well as its versatility and adaptability.
Very Narrow Aisle (VNA) racking
VNA pallet racking is an adaptation of the adjustable pallet racking system, but with better use of the available space in the warehouse. The width of the work aisles is reduced so as to reduce the necessary floor space for their installation, and direct access is maintained to all the pallets stored.
It needs special narrow aisle forklifts to move about and operate in the warehouse.
Double deep pallet racking
Double deep pallet racking is another adaptation of the adjustable pallet racking system, modified to increase the storage capacity.
In this case, optimisation is achieved by adding an extra position for pallets at the back of the racking, storing the unit loads at 2 depths. The advantage is the greater storage capacity, but the disadvantage is loss of selectivity or direct access to each and all of the unit loads.
Drive In and Drive Through Compact Systems
Both Drive In and Drive Through Compact Racking are a type of high-density pallet racking system that optimise the available space in the warehouse.
In this system, work aisles are eliminated, and the forklift enters the racking structure for loading and unloading operations.
Drive In racking works according to the LIFO system with a single entry and exit aisle for the forklift, while the Drive Through system works with the FIFO method and has an access aisle for loading and the opposite end for unloading pallets.
Live Storage for pallets (FIFO)
FIFO Live Storage Pallet Racking is a storage system that has a compact structure and lines of rollers with a downward incline to move the pallets from where they are deposited at one end of the racking to the other end at the back.
It is a FIFO system, where the first pallet to be loaded is the first one to be removed, enabling perfect stock rotation in the warehouse.

Push-Back Pallet Racking
Push-Back Pallet Racking has a very similar structure to FIFO live storage systems, but here the pallets are stored according to the LIFO (Last in, First out) method.
When the forklift loads a new pallet, it pushes the previous pallet to the back. The Push-Back system also has beds of rollers or trolleys, which enable the displacement of the pallet through pushing.
Mobile Pallet Racking
In Mobile Pallet Racking systems the structure is installed next to some chassis guided by rails on the floor, which enables the lateral displacement of the racking modules.
It is a compact structure which, thanks to the displacement of the racking blocks, allows work aisles to be opened for the operation of forklifts.