The Wilson Model, also known as the EOQ (Economic Order Quantity) system, is a very widely used stock management method to reduce inventory costs in a warehouse.
It is one of the simplest stock management models to implement, which is why it is so widely used. It focuses on calculating the appropriate quantity of each product or raw material order of a company to reduce its inventory costs to a minimum.
We will look at this method below, breaking down its characteristics, advantages, disadvantages and applications:
What is the Wilson method or EOQ (Economic Order Quantity) system and when does it apply?
This model became popular in 1934 with the publication of an article by R.H. Wilson, after whom the model is named, but it was developed originally by the engineer Ford Whitman Harris when he worked in the company Westinghouse Corporation.
The method was created with the clear objective of systematising the goods that are periodically held in the warehouse and defining the quantity and date on which orders must be placed with suppliers.
Although this system is commonly used to systematise the purchase of raw materials, it is applicable to optimising the purchase of any product required by the company provided purchasing costs can be determined in order and storage terms.
The method is simple and based on a formula that helps to determine when and in what quantity company orders must be placed, taking into account demand and the company’s minimum safety stock.
To develop the model and calculation correctly, full knowledge is required of the company’s logistics processes and the various stages of the supply chain and decision-making process.
Basic assumptions of the Wilson model
To develop the EOQ method, the following basic conditions or assumptions must be fulfilled in the company, otherwise the calculations cannot be made accurately:
- It is based on the assumption that the company’s demand is known and is independent and without major fluctuations during the year, so is therefore constant.
- The unit cost of each product or purchase must also fulfil these conditions, being known and fixed throughout the year. It is not valid therefore for seasonal products.
- Storage costs are also known and depend on the level of stock.
- Potential purchase or order volume discounts are not considered.
- The supplier’s supply and loading times are also considered constant and are known.
- It is assumed that there is no stock depletion and that at any time any product quantity can be requested from the supplier.

Economic Order Quantity Formula (Wilson Model)
To calculate the model formula, the following terms must be determined:
- Q: Optimum quantity of each order
- K: Cost of each order
- D: Annual product or raw material demand
- G: Storage cost of each unit
With these terms present, we arrive at the simplified formula that defines the optimum quantity for each company order (Q):

Practical example of the EOQ model (Economic Order Quantity)
Applying the above theoretical formula to a practical example, let us assume that the fictitious company Sillas Grandes World SL distributes office chairs in its country and wants to know the optimum product quantity that it should place in its orders.
If this company has an annual demand of 6,000 chairs (D), the cost of each order or purchase, with all the resulting expenses (K), is €300, and the annual storage cost of each chair (G) is €5, what would be the optimum quantity of each order (Q)?
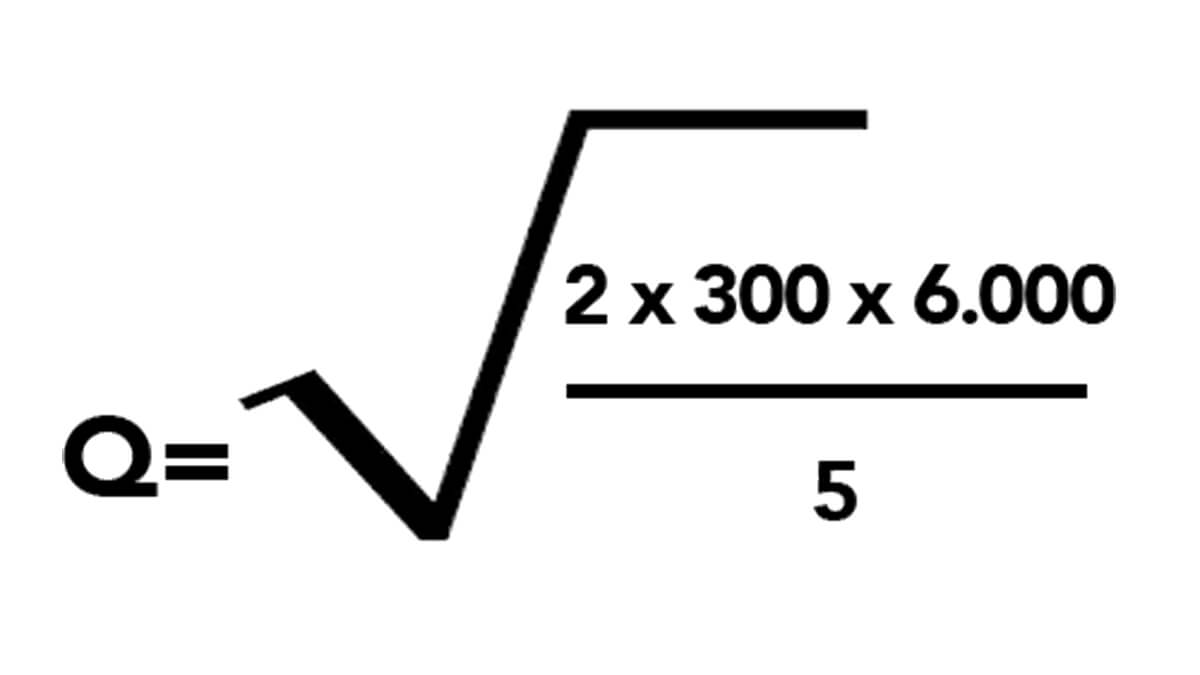
Following this formula, the optimum quantity for the company Sillas Grandes World SL would be 848.52 units for each order placed, so it would have to place 7.07 orders per year.
With these results, and following the Wilson or EOQ method, the company would achieve an optimum inventory level throughout its warehouse without incurring any excess stock or stock depletion.
Advantages of the Economic Order Quantity Method (EOQ)
The Wilson or EOQ method is widely used internationally for its advantages over other types of methods.
The main benefits of this system can be summarised as follows:
- Ease and simplicity of use compared to other types of similar models.
- The EOQ method helps optimise storage and purchasing costs.
- It helps to avoid overstock situations in the warehouse.
- Defining the correct product quantity to be acquired helps to avoid stock depletion.
- The EOQ (Economic Order Quantity) model has widely demonstrated results in situations that fulfil the aforementioned assumptions.
Disadvantages of the EOQ or Wilson method
The main disadvantages of the Wilson model or EOQ system lie in the same above-considered assumptions, as they limit its application and make the model less practical for real situations with non-constant terms.
The main disadvantages of the model in detail are:
- The assumptions make the model impractical or not realistic for many companies due to its characteristics. The constant demand assumption means that the EOQ model is not useful for companies with seasonal, one-off or irregular demands, or may lead to errors in case of a drastic change in the customer’s habits.
- The fact that purchase volume discounts are not considered leaves a very relevant variable out of the equation which may offset storage costs.
- The assumption of immediacy in the replenishment of inventory is not entirely realistic either, and without considering this variable there may be stock depletion situations that will need to be carefully considered when developing the model.
If you require advice on choosing the most appropriate storage system according to your warehouse needs, to optimise the available space or to implement a storage capacity expansion project, our team will be delighted to help you. Contact us here.




